

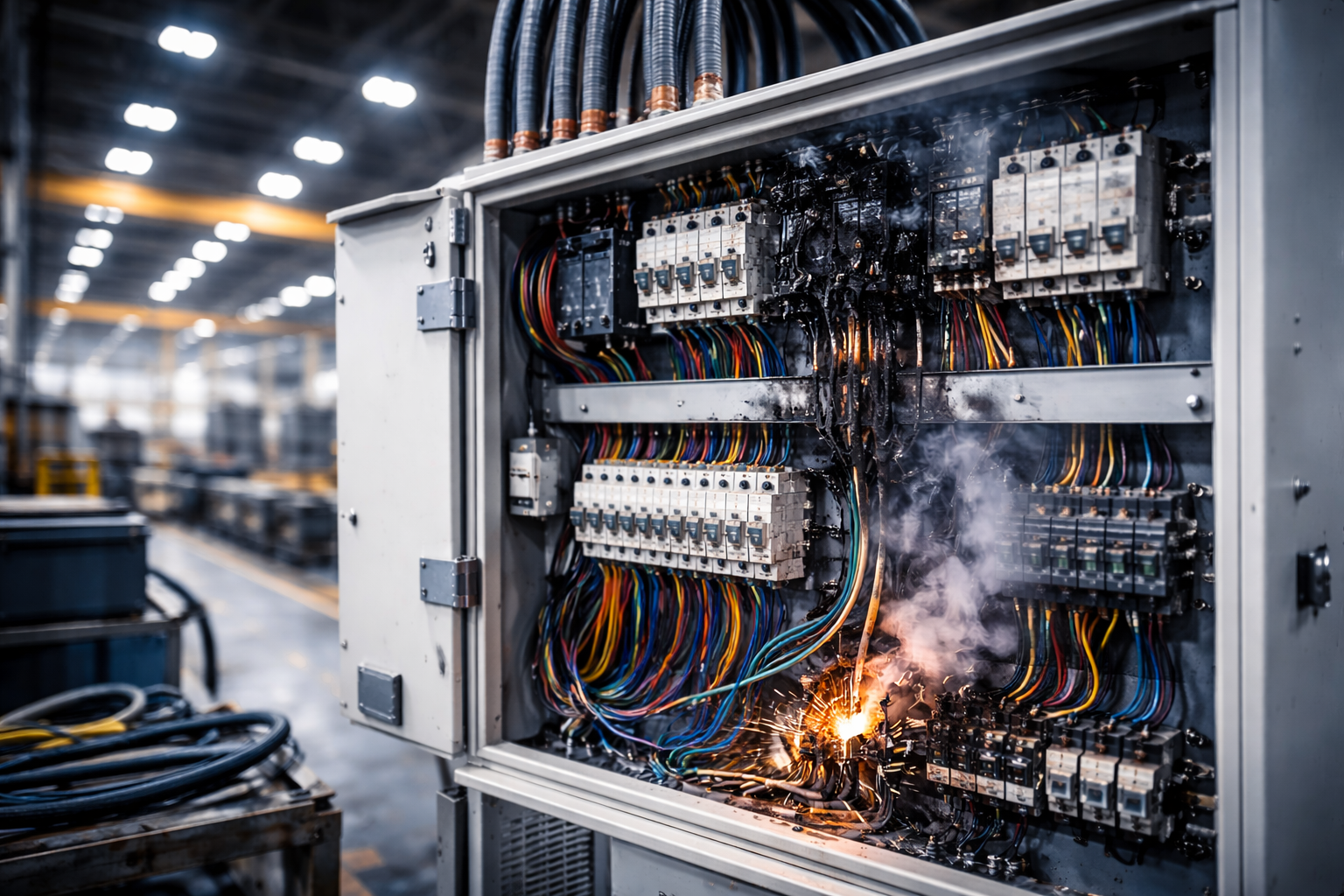
Electrical panels are the backbone of industrial power distribution. From running automated production lines to protecting critical equipment, their reliability directly affects safety, productivity, and operational continuity. Yet electrical panel failures remain one of the most common causes of unplanned downtime in industrial facilities worldwide. This article provides an educational breakdown of the most common causes of electrical panel failures in industrial environments, categorized into environmental, design, installation, and operational factors. Using real-world examples and industry references, it explains why failures occur and how they can be prevented.
Why Electrical Panel Failures Matter
When an electrical panel fails, the impact is rarely limited to a single component. Consequences often include:
According to industry reports and technical literature from companies such as Siemens, Schneider Electric, and ABB, many failures are preventable when root causes are properly understood and addressed early.
Primary Categories of Electrical Panel Failures
Most industrial electrical panel failures fall into four main categories:
Each category plays a critical role in long-term panel reliability.
1. Environmental Factors: When the Site Dictates Performance
Industrial environments are rarely controlled or clean. Electrical panels are often exposed to:
Thermal Stress and Heat Build-Up
Excessive heat is one of the leading causes of electrical panel failure. Elevated temperatures accelerate insulation breakdown, reduce component life, and increase contact resistance.
Real-world example:
In a steel processing plant, control panels rated for 40°C were consistently exposed to ambient temperatures exceeding 55°C. Within two years, multiple contactors and power supplies failed, resulting in repeated production stoppages.
Manufacturers such as ABB and Siemens explicitly recommend thermal derating and adequate ventilation for panels operating in high-temperature environments.
Moisture, Condensation, and Corrosion
Moisture ingress can occur even in panels with high IP ratings if sealing, installation, or maintenance is inadequate. Condensation inside enclosures can cause:
In food processing and pharmaceutical plants, washdown operations frequently expose panels to moisture unless enclosure selection and sealing are carefully engineered.
2. Design and Engineering Limitations
Panel reliability is heavily influenced by decisions made during the design stage.
Undersized or Improperly Rated Components
Using components rated too close to normal operating limits leaves little margin for load variations, ambient temperature rise, or future expansion.
Industry insight:
Schneider Electric’s application guides consistently recommend designing panels with spare capacity to handle peak loads and long-term growth.
Poor Internal Layout and Heat Dissipation
Crowded layouts, improper spacing between heat-generating devices, and lack of airflow can cause localized hot spots even when total load calculations appear acceptable.
In several automotive manufacturing plants, thermal imaging audits have revealed critical hotspots inside panels that were otherwise compliant on paper.
3. Installation Errors: Small Mistakes with Big Consequences
Even well-designed panels can fail prematurely due to improper installation.
Loose Electrical Connections
Loose terminations are one of the most common and dangerous installation-related issues. They increase resistance, generate heat, and eventually lead to arcing or component failure.
Case example:
A packaging facility experienced repeated breaker trips due to overheating. Investigation showed that cable lugs were not torqued to manufacturer specifications during installation.
Improper Grounding and Earthing
Incorrect or inadequate grounding can cause electrical noise, equipment malfunction, and increased fault risk. Many failures attributed to “component defects” are later traced back to grounding errors.
Leading manufacturers like Siemens emphasize grounding integrity as a foundational requirement for panel performance and safety.
4. Operational and Maintenance-Related Causes
Electrical panels are often treated as “fit-and-forget” equipment, which significantly increases failure risk.
Lack of Preventive Maintenance
Common maintenance-related issues include:
In a chemical manufacturing plant, routine thermal scanning identified a breaker operating far above normal temperature, allowing replacement before a catastrophic failure occurred.
Comparison Table: Causes and Preventive Measures
|
Failure Category |
Typical Causes |
Impact on Operations |
Preventive Approach |
|
Environmental |
Heat, moisture, dust, corrosion |
Insulation failure, short circuits |
Correct enclosure rating, ventilation |
|
Design |
Undersized components, poor layout |
Overheating, reduced lifespan |
Load analysis, thermal design |
|
Installation |
Loose connections, poor grounding |
Arcing, equipment damage |
Torque-controlled installation |
|
Maintenance |
Dust build-up, aging components |
Unexpected downtime |
Scheduled inspections |
Industry Practices from Leading Companies
Siemens
Focuses on design standards, thermal management, and digital diagnostics to identify early warning signs of failure.
Schneider Electric
Provides detailed guidance on enclosure selection, heat calculations, and preventive maintenance strategies.
ABB
Emphasizes robust component selection and predictive maintenance to reduce downtime in harsh environments.
These companies consistently highlight that failures are rarely caused by components alone, but by the ecosystem in which they operate.
Conclusion
Electrical panel failures in industrial environments are rarely sudden or random events. In most cases, they are the result of cumulative stress caused by environmental exposure, design compromises, installation shortcuts, and insufficient maintenance.
Understanding these root causes allows organizations to shift from reactive repairs to proactive prevention. By designing panels for real operating conditions, installing them with discipline, and maintaining them regularly, industries can significantly improve safety, reliability, and uptime.
Electrical panels are not just assemblies of components; they are engineered systems that require thoughtful design, careful execution, and ongoing attention throughout their lifecycle.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the most common cause of electrical panel failure?
Thermal stress caused by heat buildup, often due to undersized components or inadequate ventilation.
2. Do IP-rated enclosures guarantee long-term reliability?
No. IP ratings address dust and water ingress but do not account for heat, vibration, or installation quality.
3. How often should industrial panels be inspected?
Visual inspections should be regular, with thermal imaging and detailed checks performed at least quarterly.
4. Can poor grounding really lead to panel failure?
Yes. Improper grounding can cause electrical noise, overheating, and increased fault risk.
5. Are branded components alone enough to prevent failures?
High-quality components help, but reliability depends equally on design, installation, and maintenance.